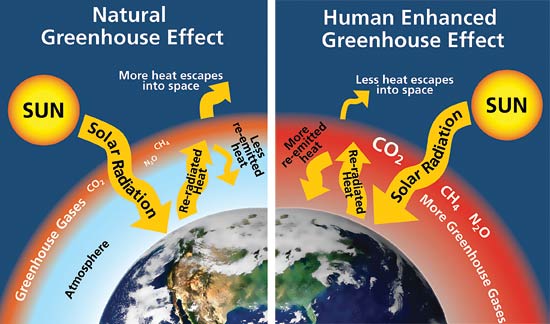
In almost all explanations of the greenhouse effect, it is somehow claimed that greenhouse gases (GHG) absorb IR radiation and therefore must heat up the atmosphere. Then, because of the heating up, the atmosphere will also radiate back more energy to the surface and heat it up.
I think that is a wrong representation of what happens.
Radiation effect of GHG
Let’s consider a volume of air that receives radiation from the earth’s surface, which has reached thermal equilibrium state. The temperature has reached a value (Teq) at which all absorbed energy is radiated out again, of course in all directions.
If we now double the amount of GHG in the volume, the added molecules will receive the same amount of radiation, so they will also end up at Teq, at which they emit as much energy as they absorb. Increasing the GHG concentration does not affect Teq.
It does increase back radiation, so when the volume is close to the surface, it will heat up that surface, as we have easily quantified in our simulation. But the air temperature will remain the same, i.c. Teq. So there is no warming of the volume.
Saturation
When the GHG concentration reaches GHG sensitive IR saturation levels, an increase of GHG no longer increases the amount of absorbed IR, while the emission still increases linearly. This disturbs the equilibrium, so the temperature has to drop.
Therefore increasing GHG concentration does not heat up the atmosphere directly. If GH gases change temperature at all, they cool it down. But they still do warm the surface by an increase of re-radiation, even if they cool down the air.
Indirect warming
There is a second hand warming effect though.
In the volume of air above the one we consider, CO2 is also doubled, leading to more re-radiation to the surface.
As explained in the Fireworks theory, part of that re-radiation is caught by the GHG molecules in our volume, thus increasing the total absorbed energy. It depends on the level of saturation for the incoming IR wavelenghts which effect is stronger: the cooling effect because of more emission or the warming effect of more absorption.
Convection
So far only the radiation aspects of the atmosphere were considered.
Let’s now see what convection does.
Low in the atmosphere, convection basically withdraws energy: molecules that have absorbed IR energy are moved to higher levels in the atmosphere, withdrawing energy from the lower levels. The GHG in the lower levels, on their way to Teq, will have “to work harder”, and will never reach Teq. So the actual temperature (Tac) in equilibrium state will be lower than Teq at the lower levels.
If you add GHG in that situation, these levels will get closer to Teq, so then an increase in GHG is heating up the air.
High in the atmosphere, convection is adding energy to the local air: molecules arriving from lower levels carry up energy that is absorbed at lower levels. There the GHG will not be able to cool the Tac till Teq, so Tac is higher than Teq. An increase in GHG will get Tac closer to Teq, so it will cool the air.
Negative feed back of combined convection and saturation
Substantial saturation only occurs with high GHG concentrations, as they exist in the lower atmosphere. So the heating effect at lower levels of CO2 combined with convection is limited by saturation, while the cooling effect at high altitudes is not.
This suggests some sort of negative feed back on the warming by a GHG increase, that needs further quantification.
This chapter has been considerably revised and extended.
The only problem I see with the re-radiation theory is that by the time IR is re-radiated, it has lost a lot of energy and is colder than the surface, its origin. So it cannot warm the surface. Heat only flows to colder things.
Energy does not get lost. This absorbed IR energy is re-emitted in all directions equally, as is explained in chapter 1.
The re-radiating molecule does not “know” what the temperature is in all surfaces it might send IR energy to. It just emits energy with T^4, according to Stefan-Bolzmann. As do the other surfaces to the molecule.
Of course the net energy transport is always from warmer to colder surfaces. That is exactly what is calculated in the spreadsheet.
I think I did not clarify very well. When I said lost, I was thinking lost to colder surrounding air. I am saying that only part of the original energy is re-radiated towards the earth and seeing as that is less than the original energy that it won’t warm the earth. The earth would be warmer than the re-radiated IR could make it. So I see no net warming effect. I think all of that re-radiated energy is repeatedly taken up by colder air at higher altitudes until it is finally radiated into space. I don’t think there is enough re-radiated energy to warm the surface measurably.
Nobody states that the re-radiated energy warms the surface. It reduces the cooling of the surface by re-emitting the most part of the emitted energy, as a semi-transparent mirror would.
If there was no back-radiation, the surface would cool down dramatically and the earth would be a snowball: we are talking about 240 W/m2 (see flow chart in chapter 5). That is more than the insolation reaching the surface.
Your idea of loosing energy to the surrounding air is not correct: we assume a semi equilibrium situation, which is reached after the system temperature has settled. In that situation, the absorbed energy by a parcel of air is by definition equal to it’s emitted energy. As long as it is not, temperature would change until both are equal and temperature reaches equilibrium state.
In the first chapters I explain how a great part of the energy that was emitted by the surface is back-radiated.
However: this is for the largest part done by water vapour, and CO2 increase does not contribute much to it (0,7%), which is calculated in chapter 4 about climate sensitivity.